GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data. GraphQL provides a complete and understandable description of the data in your API, gives clients the power to ask for exactly what they need and nothing more, makes it easier to evolve APIs over time, and enables powerful developer tools.
Today we will go through the setup of a GraphQL server in .NET using Hot Chocolate. We are going to cover GraphQL Queries and Mutations using the code-first approach. Run the following command to setup the project:
dotnet new web -n api
dotnet new sln -n graphql-sandbox
dotnet sln add api
dotnet add api package HotChocolate.AspNetCore --version 12.14.0
Add a new file Post.cs using the following code:
public class Post
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Title { get; set; }
public string Body { get; set; }
}
Next, add a file Repository.cs with the following code (this class will simulate our data storage):
public class Storage
{
public List<Post> Posts { get; set; } = new List<Post>();
}
Object Types
The most important type in a GraphQL schema is the Object Type. Object types are used in GraphQL to define the data structures of your application as well as the relationships between objects. Add a new file PostType.cs with the following content:
public class PostType : ObjectType<Post>
{
protected override void Configure(IObjectTypeDescriptor<Post> descriptor)
{
descriptor
.Field(f => f.Title)
.Type<StringType>();
descriptor
.Field(f => f.Body)
.Type<StringType>();
descriptor
.Field(f => f.Id)
.Type<IdType>();
}
}
Queries
A Query is a GraphQL operation used to fetch data. Add a file PostQueries.cs with the following content:
public class Query
{
public List<Post> GetPosts([Service] Storage storage)
{
return storage.Posts;
}
public Post? GetPost(Guid id, [Service] Storage storage)
{
return storage.Posts.FirstOrDefault(post=>post.Id==id);
}
}
Add a new file PostQueriesType.cs with the folowing content:
public class PostQueriesType : ObjectType<PostQueries>
{
protected override void Configure(IObjectTypeDescriptor<PostQueries> descriptor)
{
descriptor
.Field(f => f.GetPost(default!, default!))
.Type<PostType>();
descriptor
.Field(f => f.GetPosts(default!))
.Type<ListType<PostType>>();
}
}
Open the Program.cs file and copy the following code:
using api;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var storage = new Storage() {
Posts = new List<Post>()
{
new Post() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), Title="My First GraphQL API", Body= "Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet." }
}
};
builder.Services.AddSingleton(storage);
builder.Services
.AddGraphQLServer()
.AddQueryType<PostQueriesType>()
;
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGraphQL();
app.Run();
Run the application with the following command:
dotnet run --project api\api.csproj --urls="http://localhost:7121"
Open the URL http://localhost:7121/graphql/ in your browser:
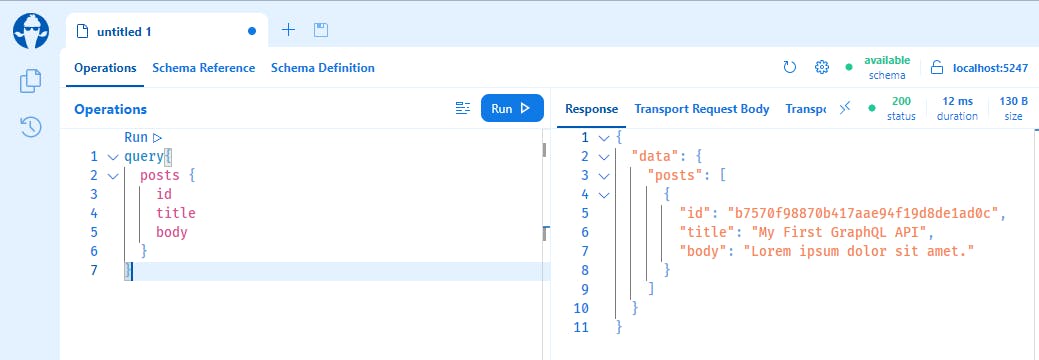
Run the following query in Banana Cake Pops:
query{
posts {
id
title
body
}
}
Mutations
A Mutation is a GraphQL operation that allows you to insert new data or modify the existing data on the server side. Add a new file PostMutations.cs with the following content:
public record AddPostInput(string Title, string Body);
public record EditPostInput(Guid Id, string Body);
public record RemovePostInput(Guid Id);
public record AddPostPayload(Post post);
public record RemovePostPayload(Post post);
public record EditPostPayload(Post post);
public class PostMutations
{
public AddPostPayload AddPost(AddPostInput input, [Service] Storage storage)
{
var post = new Post() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), Body = input.Body, Title = input.Title };
storage.Posts.Add(post);
return new AddPostPayload(post);
}
public RemovePostPayload RemovePost(RemovePostInput input, [Service] Storage storage)
{
var post = storage.Posts.Single(post => post.Id == input.Id);
storage.Posts.Remove(post);
return new RemovePostPayload(post);
}
public EditPostPayload? EditPost(EditPostInput input, [Service] Storage storage)
{
var post = storage.Posts.Single(post => post.Id == input.Id);
post.Body = input.Body;
return new EditPostPayload(post);
}
}
And add its corresponding PostMutationsType.cs file with the following code:
public class PostMutationsType : ObjectType<PostMutations>
{
protected override void Configure(
IObjectTypeDescriptor<PostMutations> descriptor)
{
descriptor.Field(f => f.AddPost(default!, default!));
descriptor.Field(f => f.RemovePost(default!, default!));
descriptor.Field(f => f.EditPost(default!, default!));
}
}
Go to the Program.cs file and update it as follows:
using api;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddSingleton(new Storage());
builder.Services
.AddGraphQLServer()
.AddQueryType<PostQueriesType>()
.AddMutationType<PostMutationsType>()
;
var app = builder.Build();
app.MapGraphQL();
app.Run();
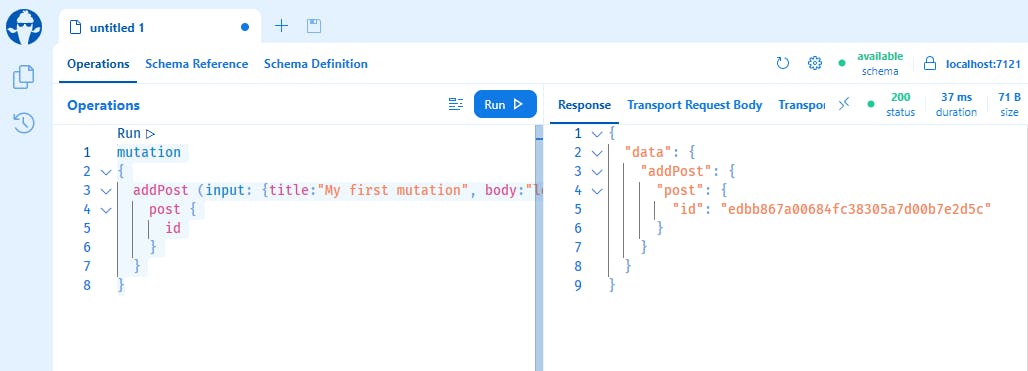
Start the application and run the following mutation to add a new post:
mutation
{
addPost (input: {title:"My first mutation", body:"lorem ipsum"}) {
post {
id
}
}
}
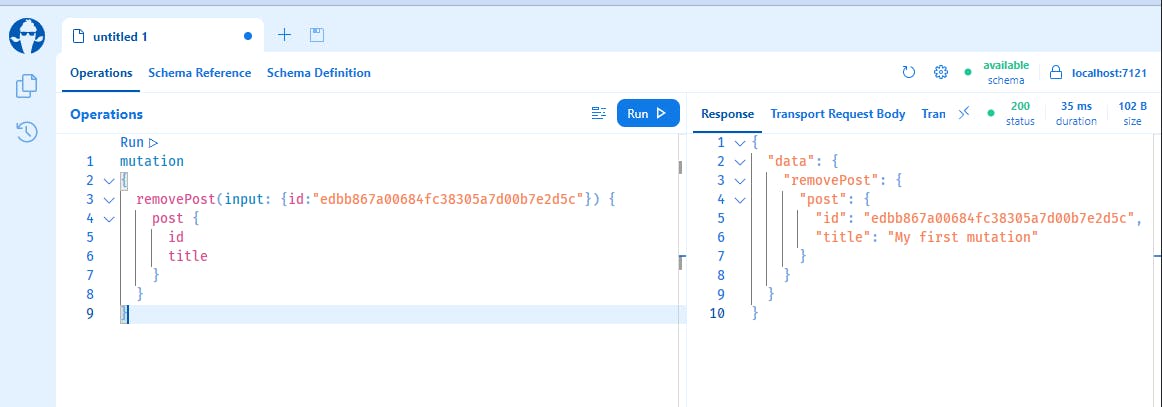
And remove your post with:
mutation
{
removePost(input: {id:"edbb867a00684fc38305a7d00b7e2d5c"}) {
post {
id
title
}
}
}
And that's it for this post. All the code is available here. Thanks, and happy coding.