Lambda layers provide a convenient way to package libraries and other dependencies that you can use with your Lambda functions. Using layers reduces the size of uploaded deployment archives and makes it faster to deploy your code.
Moving the concept above to the .NET ecosystem, Lambda Layers allow us to put dependencies (assemblies) outside of the deployment package, which reduces the size of the .zip file that has to be uploaded whenever we deploy a function. This approach is useful when working with large dependencies or when multiple functions share the same dependencies. Sounds easy, but how to take advantage of this feature in .NET? Runtime package store is the answer to that question:
Starting with .NET Core 2.0, it's possible to package and deploy apps against a known set of packages that exist in the target environment
Therefore, the steps to use Lamba Layers in .NET are:
Create the Lambda Layer with all the dependencies we want.
In our Lambda Function, add a reference to the Lambda Layer.
Deploy our Lambda Function without including the dependencies included in the Lambda Layer.
Prerequisites
An IAM User with programmatic access.
Install AWS CLI.
Install the Amazon Lambda Templates (
dotnet new -i Amazon.Lambda.Templates).Install the Amazon Lambda Tools (
dotnet tool install -gAmazon.Lambda.Tools).An s3 bucket (
aws s3api create-bucket --bucket <MY_BUCKET_NAME> --region <MY_REGION> --create-bucket-configuration LocationConstraint=<MY_REGION>).
Creating a Lambda Function
Disclaimer: .NET Core 3.1 will be used in this post until we know why it does not work with .NET 6.
Run the following commands to create a Lambda Function:
dotnet new lambda.EmptyFunction -n HelloWorldApi -o .
dotnet add src/HelloWorldApi package Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents
Update the HelloWorldApi.csproj file as follow:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<TargetFramework>netcoreapp3.1</TargetFramework>
<Nullable>enable</Nullable>
<GenerateRuntimeConfigurationFiles>true</GenerateRuntimeConfigurationFiles>
<AWSProjectType>Lambda</AWSProjectType>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents" Version="2.6.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.Core" Version="2.1.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson" Version="2.3.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
Update the Function.cs file as follows:
using Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents;
using Amazon.Lambda.Core;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
[assembly: LambdaSerializer(typeof(Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer))]
namespace HelloWorldApi
{
public class Function
{
public async Task<APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse> FunctionHandler(APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyRequest input, ILambdaContext context)
{
return new APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse
{
Body = @"{""Message"":""Hello world!""}",
StatusCode = 200,
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "application/json" } }
};
}
}
}
Create a template.xml file (AWS SAM) with the following content:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: >
Lambda Layers
Resources:
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Timeout: 60
MemorySize: 512
Runtime: dotnetcore3.1
Architectures:
- x86_64
Handler: HelloWorldApi::HelloWorldApi.Function::FunctionHandler
CodeUri: ./src/HelloWorldApi/
Events:
ListPosts:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /
Method: get
Let's deploy the Lambda Function to see the size of the package:
dotnet lambda deploy-serverless --region <MY_REGION> -t template.yaml -sb <MY_BUCKET_NAME>
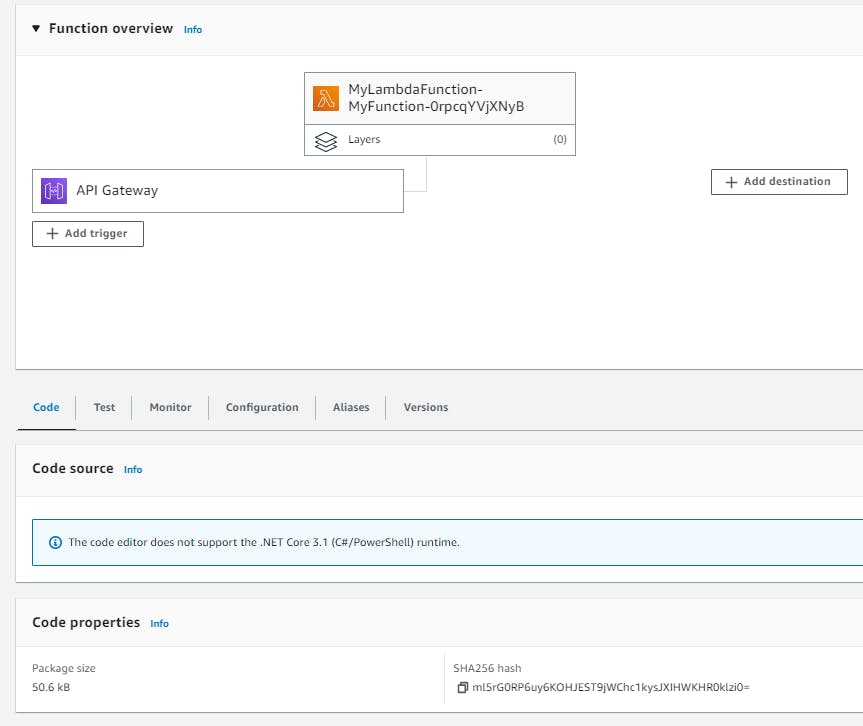
The package size, without Lambda Layers, is around 50 Kb.
Creating a Lambda Layer
Create a file named packages.csproj as follows:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
<PropertyGroup>
<GenerateRuntimeConfigurationFiles>true</GenerateRuntimeConfigurationFiles>
<AWSProjectType>Lambda</AWSProjectType>
</PropertyGroup>
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents" Version="2.6.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.Core" Version="2.1.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson" Version="2.3.0" />
</ItemGroup>
</Project>
Run the following command:
dotnet lambda publish-layer MyDotNetLambdaLayer31 -sb <MY_BUCKET_NAME> --layer-type runtime-package-store --package-manifest packages.csproj --framework netcoreapp3.1 --region <MY_REGION>
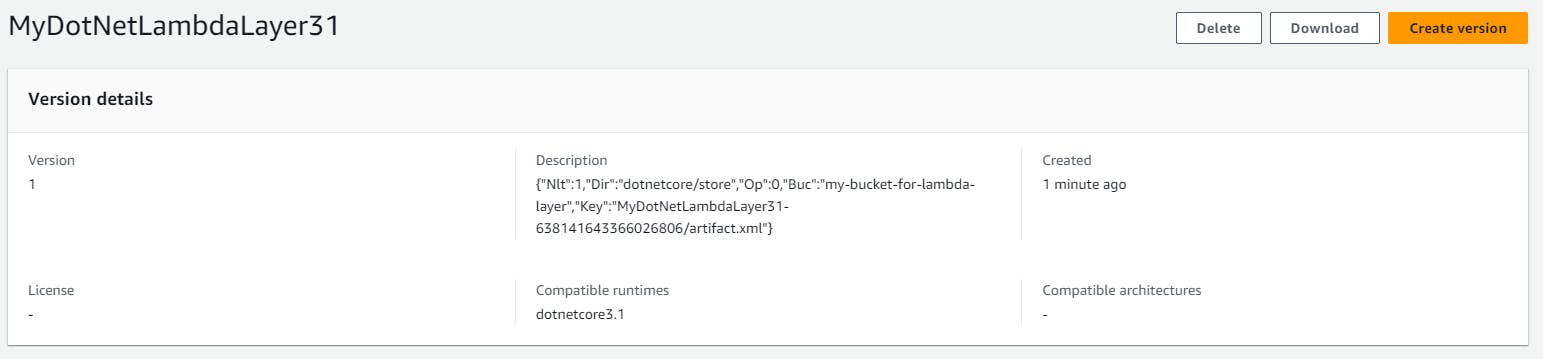
To inspect the Lambda Layer, run the command: dotnet lambda get-layer-version --arn <MY_LAMBA_LAYER_ARN>. The result will be something like this:
Layer ARN: <MY_LAMBA_LAYER_ARN>
Version Number: 1
Created: 3/11/2023 3:45 PM
License Info:
Compatible Runtimes: dotnetcore3.1
Layer Type: .NET Runtime Package Store
.NET Runtime Package Store Details:
Manifest Location: s3://<MY_BUCKET_NAME>/MyDotNetLambdaLayer31-638141643366026806/artifact.xml
Packages Optimized: False
Packages Directory: /opt/dotnetcore/store
Manifest Contents
-----------------------
<StoreArtifacts>
<Package Id="Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents" Version="2.6.0" />
<Package Id="Amazon.Lambda.Core" Version="2.1.0" />
<Package Id="Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson" Version="2.3.0" />
</StoreArtifacts>
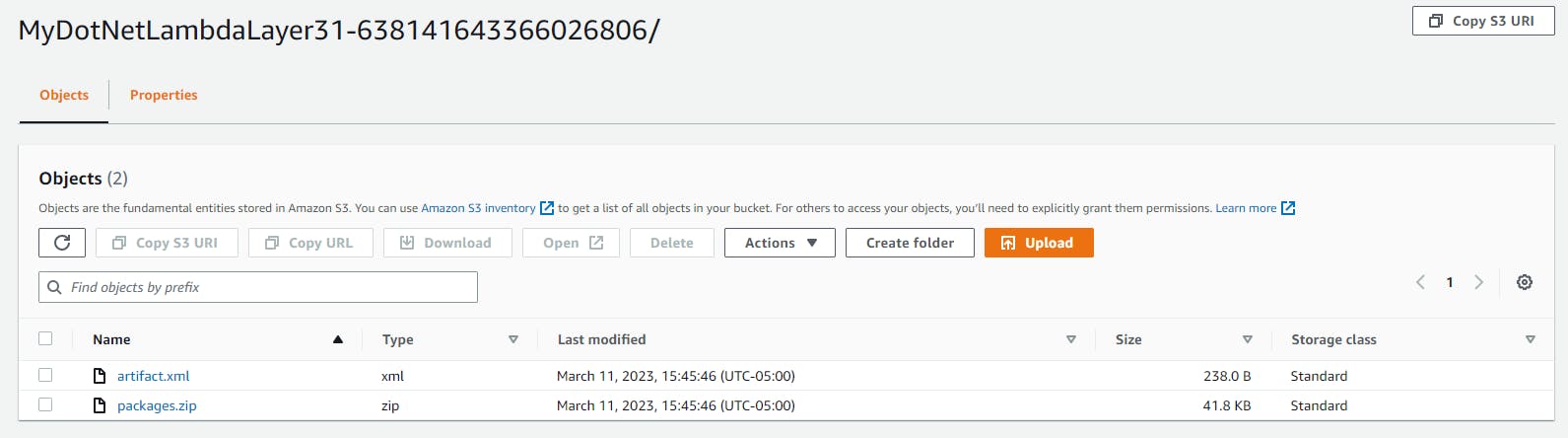
As we are using the Runtime package store in the background, the artifact.xml file contains the list of all the packages in our store. The package.zip has all the assemblies and, unzipped, represents the content of the Lambda Layer.
Using the Lambda Layer
Modify the template.xml as follows:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: >
Lambda Layers
Resources:
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Timeout: 60
MemorySize: 512
Runtime: dotnetcore3.1
Architectures:
- x86_64
Handler: HelloWorldApi::HelloWorldApi.Function::FunctionHandler
CodeUri: ./src/HelloWorldApi/
Layers :
- <MY_LAMBA_LAYER_ARN>
Events:
ListPosts:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /
Method: get
Run dotnet lambda deploy-serverless --region <MY_REGION> -t template.yaml -sb <MY_BUCKET_NAME> to update the Lambda Function:
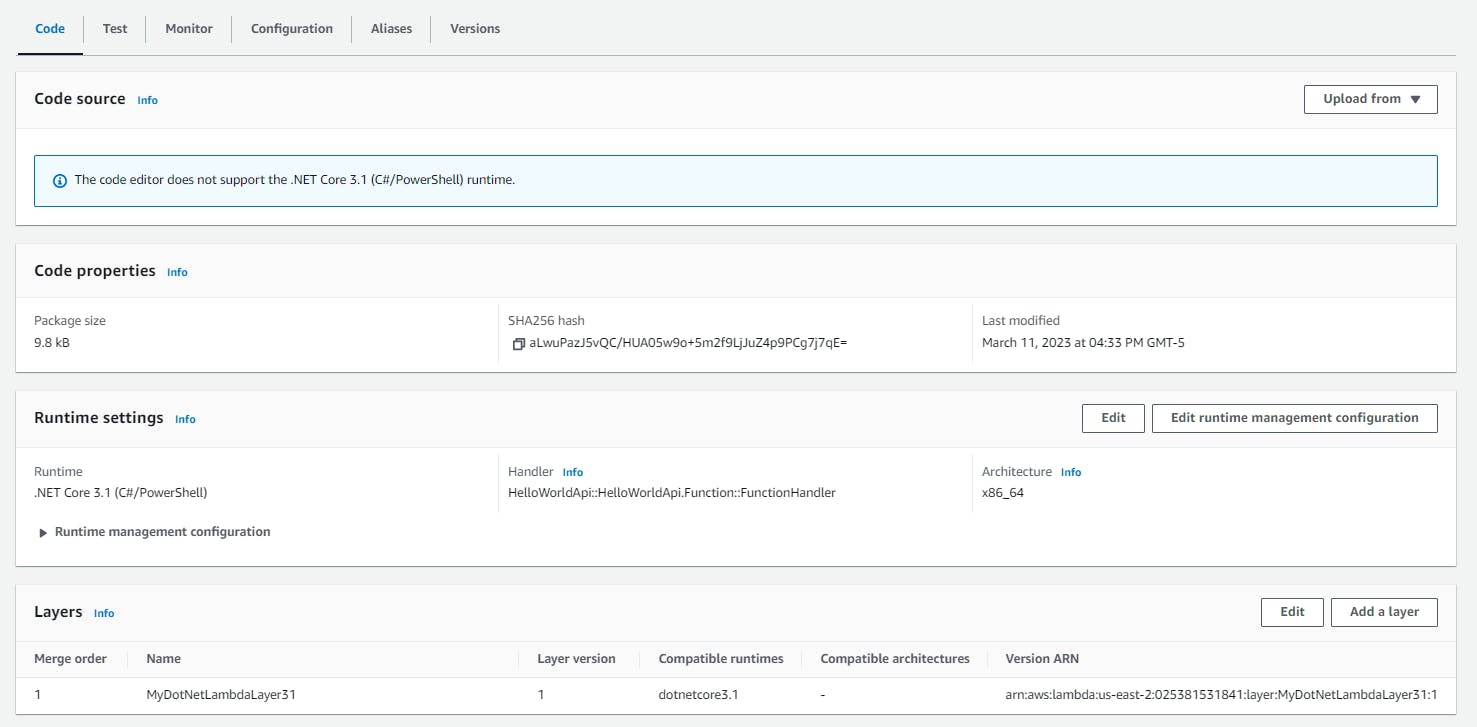
Now, the package size is around 10 Kb. But what exactly is going on here?
At the beginning of the deployment, the Lambda Layer was inspected and the
artifact.xmlfile was downloaded.The
artifact.xmlfile was used in thedotnet publishcommand, which told it not to include packages listed there.The
DOTNET_SHARED_STOREenvironment variable was added to the Lambda Function with the value/opt/dotnetcore/store/.When your Lambda Function runs, the Lambda Layer will be downloaded and made available to your Lambda Function at runtime, allowing you to use its dependencies.
For more information about Lambda Layers in .NET, follow this link. The code is available here. Thank you, and happy coding.

