Serverless computing has gained popularity in the last few years primarily because it allows a true platform-as-a-service environment, letting developers focus on coding rather than back-end operations. Under this context, AWS Lambda is one of the best alternatives to start using this hosting model for our .NET 6 applications.
Prerequisites
Tools
Install the Amazon Lambda Templates:
dotnet new -i Amazon.Lambda.Templates
Now we can see the list of AWS Lambda Templates installed running this command dotnet new --list --tag lambda:
Template Name Short Name Language Tags
---------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------- -------- ---------------------
Empty Top-level Function lambda.EmptyTopLevelFunction [C#] AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda Annotations Framework (Preview) serverless.Annotations [C#] AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda ASP.NET Core Minimal API serverless.AspNetCoreMinimalAPI [C#] AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda ASP.NET Core Web API serverless.AspNetCoreWebAPI [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda ASP.NET Core Web API (.NET 6 Container Image) serverless.image.AspNetCoreWebAPI [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda ASP.NET Core Web Application with Razor Pages serverless.AspNetCoreWebApp [C#] AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda Custom Runtime Function (.NET 6) lambda.CustomRuntimeFunction [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Detect Image Labels lambda.DetectImageLabels [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Empty Function lambda.EmptyFunction [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Empty Function (.NET 6 Container Image) lambda.image.EmptyFunction [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Empty Serverless serverless.EmptyServerless [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda Empty Serverless (.NET 6 Container Image) serverless.image.EmptyServerless [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda Giraffe Web App serverless.Giraffe F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Lambda Simple Application Load Balancer Function lambda.SimpleApplicationLoadBalancerFunction [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple DynamoDB Function lambda.DynamoDB [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple Kinesis Firehose Function lambda.KinesisFirehose [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple Kinesis Function lambda.Kinesis [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple S3 Function lambda.S3 [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple SNS Function lambda.SNS [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Lambda Simple SQS Function lambda.SQS [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Lex Book Trip Sample lambda.LexBookTripSample [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Order Flowers Chatbot Tutorial lambda.OrderFlowersChatbot [C#] AWS/Lambda/Function
Serverless Detect Image Labels serverless.DetectImageLabels [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Serverless Simple S3 Function serverless.S3 [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Serverless WebSocket API serverless.WebSocketAPI [C#] AWS/Lambda/Serverless
Step Functions Hello World serverless.StepFunctionsHelloWorld [C#],F# AWS/Lambda/Serverless
We can install the AWS Toolkit for Visual Studio to have the same templates installed.
Install the Amazon Lambda Tools:
dotnet tool install -g Amazon.Lambda.Tools
Simple HTTP API
Run the following commands to create the project and solution:
dotnet new lambda.EmptyFunction -n SimpleHTTPAPI -o .
dotnet new sln -n aws-lambda-sandbox
dotnet sln add --in-root src/SimpleHTTPAPI
Open the solution in your Visual Studio and add the following Nuget package to the project:
Modify the Function.cs file as follows:
using Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents;
using Amazon.Lambda.Core;
using System.Net;
using System.Text.Json;
[assembly: LambdaSerializer(typeof(Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer))]
namespace SimpleHTTPAPI;
public class Function
{
public APIGatewayProxyResponse FunctionHandler(APIGatewayProxyRequest request, ILambdaContext context)
{
context.Logger.LogInformation("Request: " + JsonSerializer.Serialize(request));
var response = new APIGatewayProxyResponse
{
StatusCode = (int)HttpStatusCode.OK,
Body = "Hello World",
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "text/plain" } }
};
return response;
}
}
Edit the original 'aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json' file to have:
{
"Information": [
"This file provides default values for the deployment wizard inside Visual Studio and the AWS Lambda commands added to the .NET Core CLI.",
"To learn more about the Lambda commands with the .NET Core CLI execute the following command at the command line in the project root directory.",
"dotnet lambda help",
"All the command line options for the Lambda command can be specified in this file."
],
"profile": "[profile]",
"region": "[region]",
"configuration": "Release",
"function-runtime": "dotnet6",
"function-memory-size": 256,
"function-timeout": 30,
"function-handler": "SimpleHTTPAPI::SimpleHTTPAPI.Function::FunctionHandler",
"function-url-enable": true,
"function-name": "SimpleHTTPAPI"
}
- [region] is the AWS Region where we will create the Lambda. An Example of a region is
us-east-2. - [profile], usually is
defaultand was defined at the moment to set up your AWS CLI.
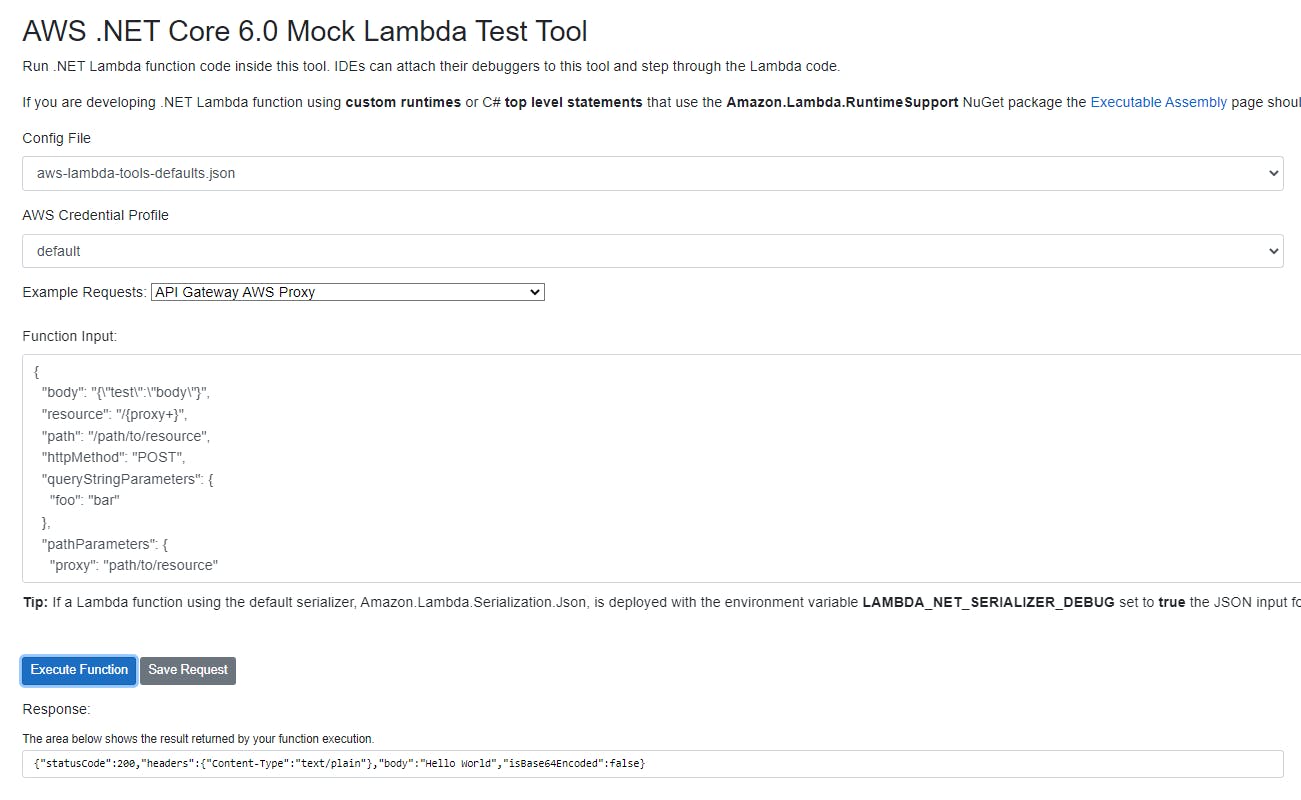
At this point, we can test the application using the Mock Lambda Test Tool profile included in the project.
Time to deploy, run the following command:
dotnet lambda deploy-function --project-location src/SimpleHTTPAPI
You will be asked which IAM role you want to use, select the *** Create new IAM Role *** option, and enter a name for the IAM Role. Finally, you will be asked what permissions to grant, select AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole. And that's it, your Lambda is up and running in AWS:
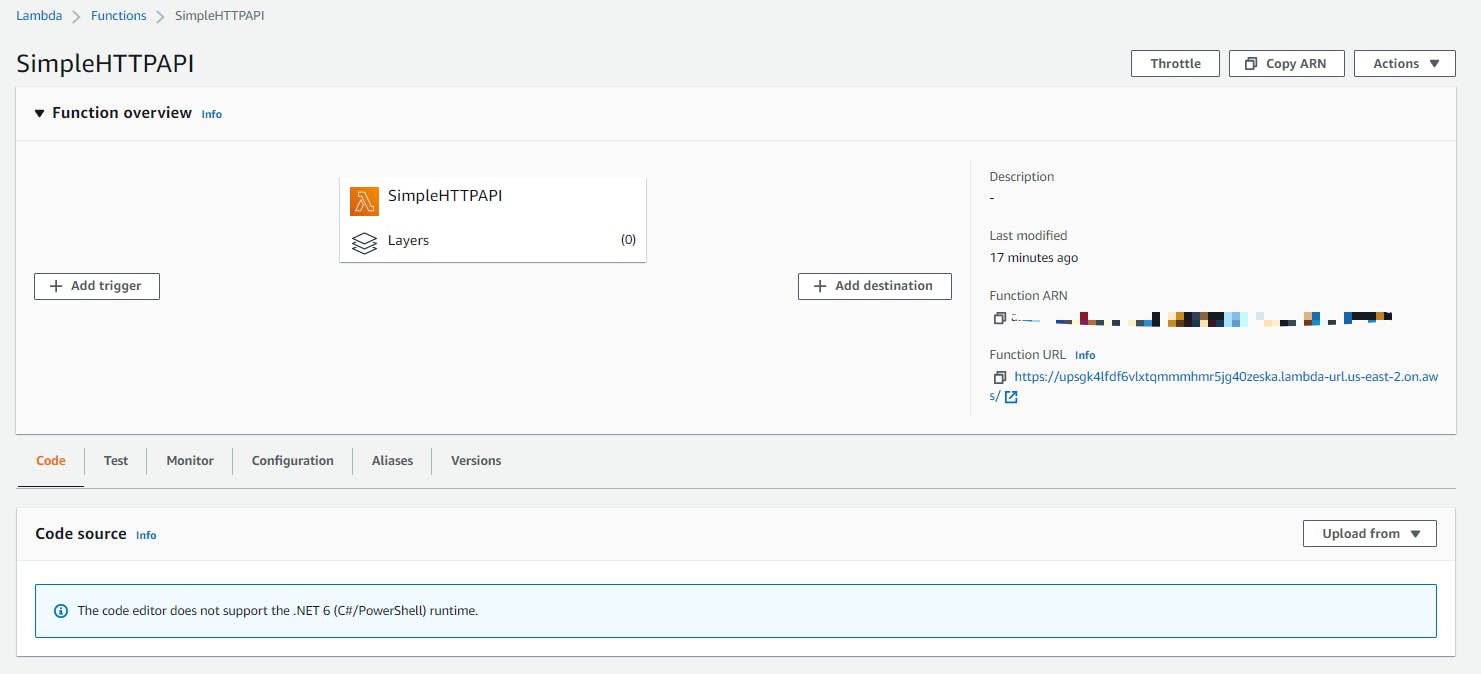
Open the Function URL to see the response of the endpoint.
ASP.NET Core Web API
Now let's see how easy it is to deploy an ASP.NET Core Web API:
dotnet new webapi -n ASPNETCoreWebAPI
dotnet sln add ASPNETCoreWebAPI
Add the following Nuget package:
Modify the Program.cs file as follows:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddControllers();
// Learn more about configuring Swagger/OpenAPI at https://aka.ms/aspnetcore/swashbuckle
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
builder.Services.AddAWSLambdaHosting(LambdaEventSource.HttpApi);
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
And add the aws-lambda-tools-defaults.json file with the following content:
{
"Information": [
"This file provides default values for the deployment wizard inside Visual Studio and the AWS Lambda commands added to the .NET Core CLI.",
"To learn more about the Lambda commands with the .NET Core CLI execute the following command at the command line in the project root directory.",
"dotnet lambda help",
"All the command line options for the Lambda command can be specified in this file."
],
"profile": "[profile]",
"region": "[region]",
"configuration": "Release",
"function-runtime": "dotnet6",
"function-memory-size": 256,
"function-timeout": 30,
"function-handler": "ASPNETCoreWebAPI",
"function-url-enable": true
}
Run the command to start the deployment and follow the steps of the previous example to complete it:
dotnet lambda deploy-function --project-location ASPNETCoreWebAPI
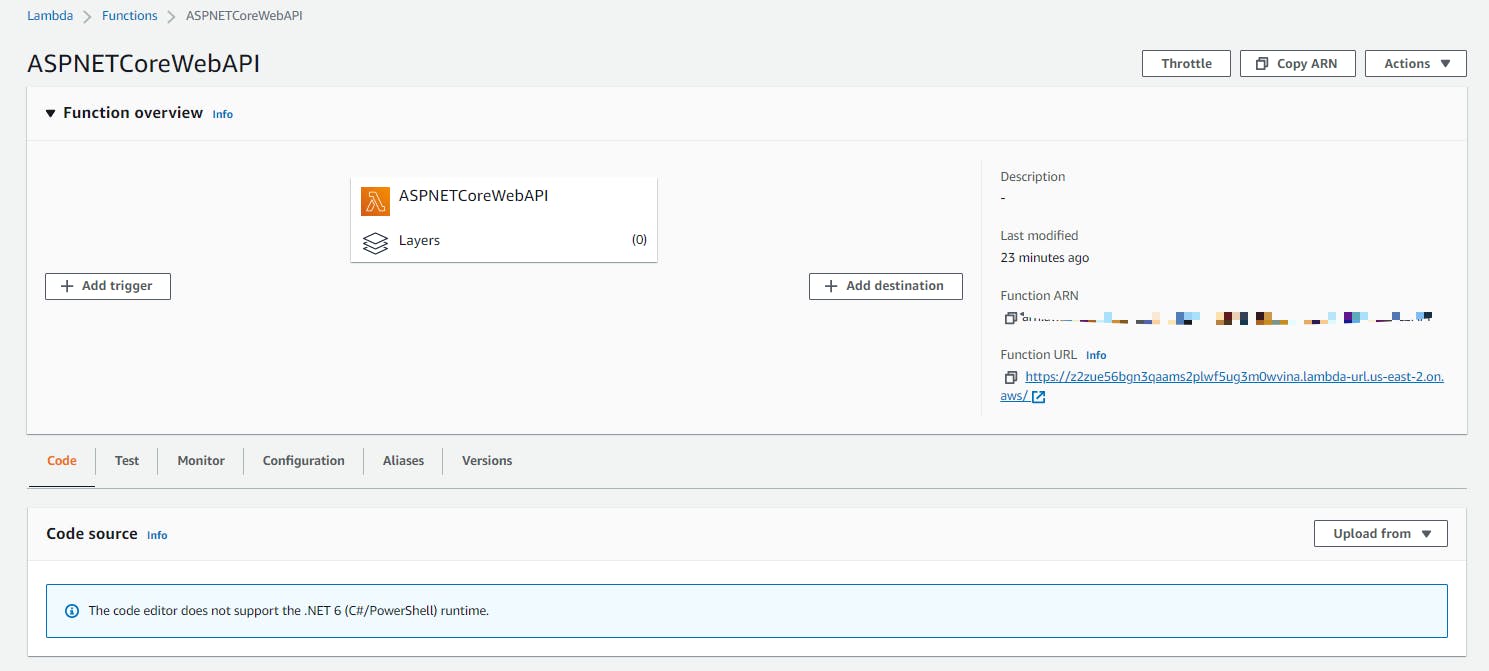
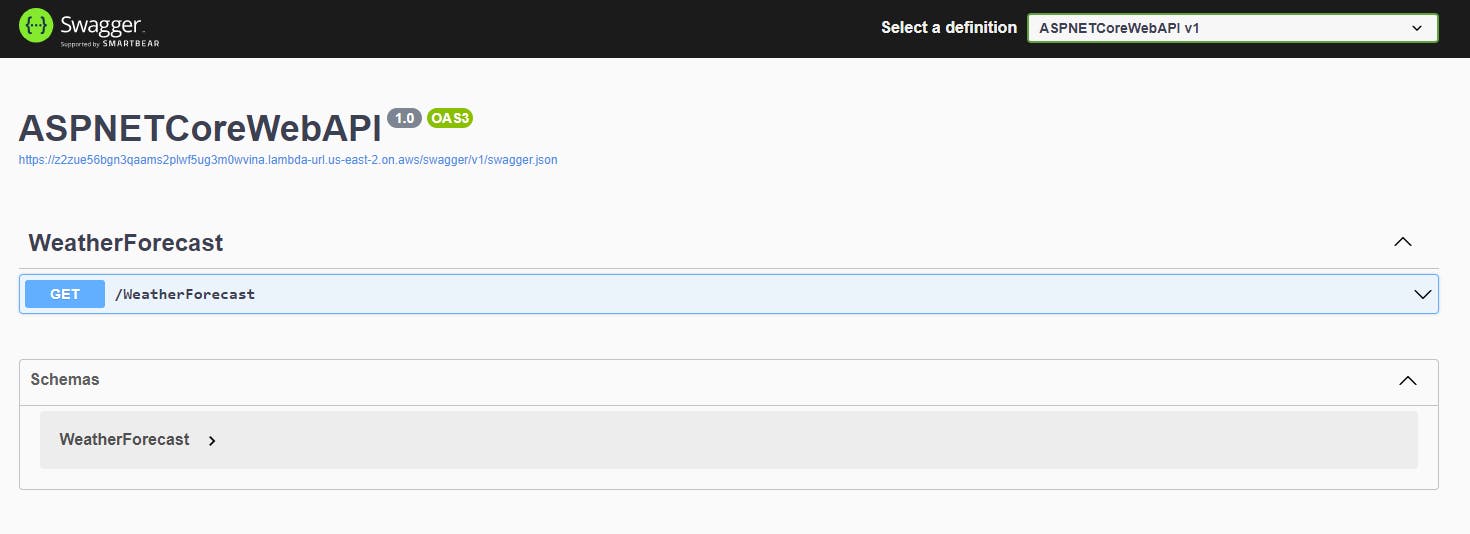
Open the Function URL to see the Swagger page of the API:
All the code is available here. Thanks and happy coding.