Table of contents
The increasing complexity of serverless applications demands an efficient way to manage and maintain their components. AWS Lambda Powertools offers a suite of utilities designed to simplify the development process, enhance observability, and implement best practices for building serverless applications. By leveraging these tools, developers can focus on their application's core functionality while enjoying the benefits of a streamlined and optimized infrastructure. AWS Lambda Powertools provides three main features:
Logging: Offers structured logs.
Tracing: Supplies a straightforward way for sending traces to AWS X-Ray.
Metrics: Provides an easy way to collect custom metrics.
Pre-requisites
Ensure you have an IAM User with programmatic access.
Install the Amazon Lambda Templates with this command:
dotnet new -i Amazon.Lambda.TemplatesInstall the Amazon Lambda Tools with this command:
dotnet tool install -g Amazon.Lambda.ToolsInstall the AWS SAM CLI.
The Lambda Function
Run the following commands to create a Lambda function:
dotnet new lambda.EmptyFunction -n HelloWorldApi -o .
dotnet add src/HelloWorldApi package Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents
dotnet new sln -n AwsPowertools
dotnet sln add --in-root src/HelloWorldApi
Open the solution, navigate to the HelloWorldApi project, and update the Function.cs file as follows:
using Amazon.Lambda.APIGatewayEvents;
using Amazon.Lambda.Core;
[assembly: LambdaSerializer(typeof(Amazon.Lambda.Serialization.SystemTextJson.DefaultLambdaJsonSerializer))]
namespace HelloWorldApi
{
public class Function
{
public async Task<APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse> FunctionHandler(APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyRequest input, ILambdaContext context)
{
var key = await KeyGenerator();
return new APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse
{
Body = $@"{{""Message"":""This is your key {key}""}}",
StatusCode = 200,
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "application/json" } }
};
}
private async Task<string> KeyGenerator()
{
await Task.Delay(Random.Shared.Next(2000));
return Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
}
}
Create a template.yml file (AWS SAM) with the following content:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: >
AWS PowerTools
Resources:
MyFunction:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Timeout: 60
MemorySize: 512
Tracing: Active
Runtime: dotnet6
Architectures:
- x86_64
Handler: HelloWorldApi::HelloWorldApi.Function::FunctionHandler
CodeUri: ./src/HelloWorldApi/
Events:
ListPosts:
Type: Api
Properties:
Path: /
Method: get
Run sam build and sam deploy --guided and follow the instructions to deploy the Lambda function.
Logging
To add the Powertools logging library to your project, execute the following command:
dotnet add src/HelloWorldApi package AWS.Lambda.Powertools.Logging
Add the following section in the template.yml file:
Globals:
Function:
Environment:
Variables:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: myfunction
POWERTOOLS_LOG_LEVEL: Debug
The complete list of environment variables (each of which can be set at the code level using the Logging attribute) is as follows:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: Sets service name used for tracing namespace, metrics dimension, and structured logging.POWERTOOLS_LOG_LEVEL: Sets logging level(Trace,Debug,Information,Warning,Error,Critical,None).POWERTOOLS_LOGGER_CASE: Override the default casing(CamelCase,PascalCase,SnakeCase) for log keys.POWERTOOLS_LOGGER_LOG_EVENT: Logs incoming event.POWERTOOLS_LOGGER_SAMPLE_RATE: Debug log sampling.
Modify the FunctionHandler implementation as follows:
[Logging(LogEvent = true)]
public async Task<APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse> FunctionHandler(APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyRequest input, ILambdaContext context)
{
Logger.LogInformation("Generating a new key");
var key = await KeyGenerator();
Logger.LogInformation(new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "Key", key } },"New key generated");
return new APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse
{
Body = $@"{{""Message"":""This is your key {key}""}}",
StatusCode = 200,
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "application/json" } }
};
}
The
Loggingattribute instructs the function to log the incoming event (when theLogEventproperty is true).Logger.LogInformation("Generating a new key")logs a simple message.Logger.LogInformation(new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "Key", key } },"New key generated")logs a message with properties.
Deploy the function to view outputs such as:
{
"cold_start": false,
"xray_trace_id": "1-648fbb32-7935059f75c9ef6705c24cb0",
"function_name": "awspowertools-MyFunction-3wYZWUsiQxv5",
"function_version": "$LATEST",
"function_memory_size": 512,
"function_arn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-2:020000000000:function:awspowertools-MyFunction-3wYZWUsiQxv5",
"function_request_id": "d833025d-8aa3-4766-9738-e5be283c233a",
"key": "0eb5d295-d646-4ba9-be06-22db05504836",
"timestamp": "2023-06-19T02:19:30.8281371Z",
"level": "Information",
"service": "myfunction",
"name": "AWS.Lambda.Powertools.Logging.Logger",
"message": "New key generated"
}
With structured logs, we can perform searches on this structured data using CloudWatch Logs Insights:
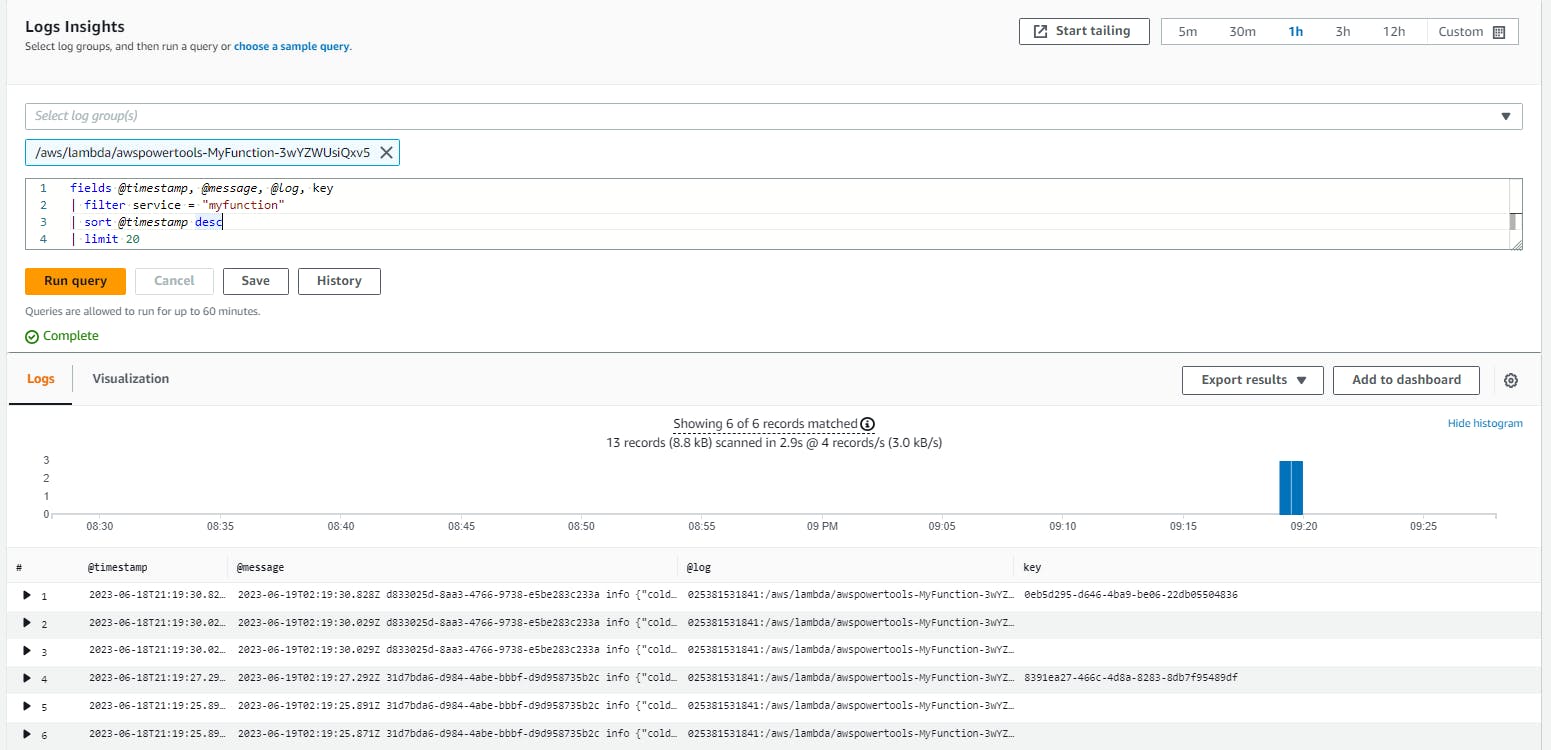
For more information, please refer to the official documentation here.
Tracing
To add the Powertools tracing library (wrapper for AWS X-Ray SDK for .NET) to your project, run the following command:
dotnet nuget add AWS.Lambda.Powertools.Tracing
Ensure that the Tracing property is activated for your AWS::Serverless::Function resource. Like the logging library, there are a set of environment variables (each of which can be set at the code level using the Tracing attribute) that we can use:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: Sets service name used for tracing namespace, metrics dimension, and structured logging.POWERTOOLS_TRACE_DISABLED: Disables tracing.POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_RESPONSE: Captures Lambda or method return as metadata.POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_ERROR: Captures Lambda or method exception as metadata.
Update the template.yml file as follows:
Globals:
Function:
Environment:
Variables:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: myfunction
POWERTOOLS_LOG_LEVEL: Debug
POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_RESPONSE: true
POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_ERROR: true
To enable PowerTools tracing for our function, add the Tracing attribute to our FunctionHandler method or to any other method:
[Logging(LogEvent = true)]
[Tracing]
public async Task<APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse> FunctionHandler(APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyRequest input, ILambdaContext context)
{
Logger.LogInformation("Generating a new key");
var key = await KeyGenerator();
Logger.LogInformation(new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "Key", key } }, "New key generated");
return new APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse
{
Body = $@"{{""Message"":""This is your key {key}""}}",
StatusCode = 200,
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "application/json" } }
};
}
[Tracing(SegmentName = "Key generator service")]
private async Task<string> KeyGenerator()
{
await Task.Delay(Random.Shared.Next(2000));
return Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
}
Deploy the function, then navigate to AWS X-Ray traces to view the results:
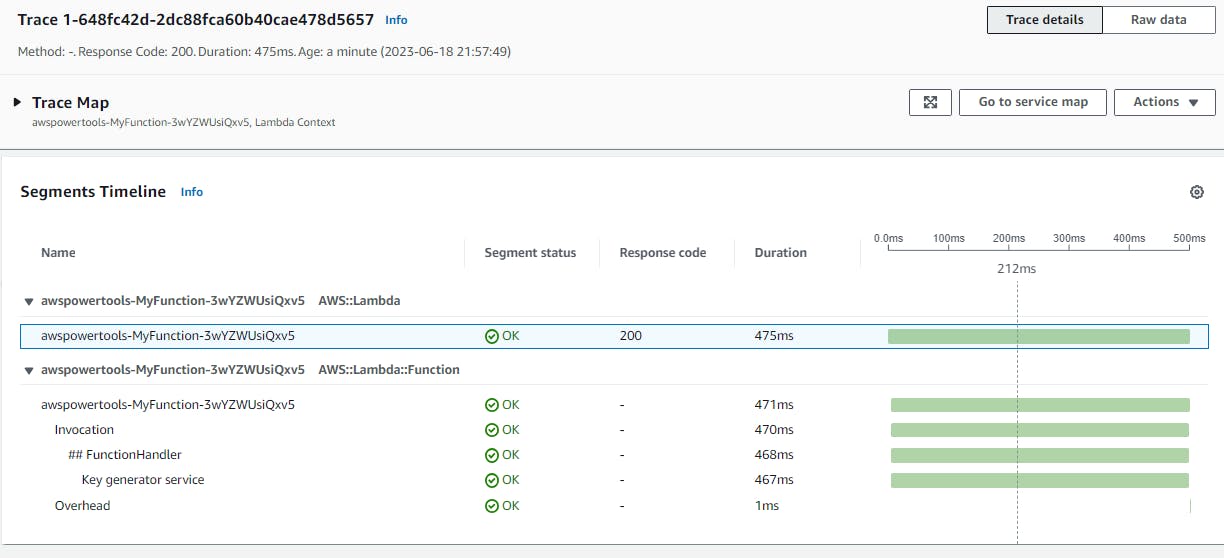
We can instrument all our AWS SDK for .NET clients by calling
AWSSDKHandler.RegisterXRayForAllServices()at the constructor level.
For more information, please refer to the official documentation here.
Metrics
To add the Powertools metrics library to your project, execute the following command:
dotnet nuget add AWS.Lambda.Powertools.Metrics
The metrics utility generates custom metrics asynchronously by logging metrics to standard output using the Amazon CloudWatch Embedded Metric Format (EMF). The set of environment variables (each of which can be set at the code level using the Metrics attribute) we can use are:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: Sets service name used for tracing namespace, metrics dimension, and structured logging.POWERTOOLS_METRICS_NAMESPACE: Sets namespace used for metrics.
Update the template.yml file as follows:
Globals:
Function:
Environment:
Variables:
POWERTOOLS_SERVICE_NAME: myfunction
POWERTOOLS_LOG_LEVEL: Debug
POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_RESPONSE: true
POWERTOOLS_TRACER_CAPTURE_ERROR: true
POWERTOOLS_METRICS_NAMESPACE: mymetrics
Modify the FunctionHandler implementation as follows:
[Logging(LogEvent = true)]
[Metrics]
[Tracing]
public async Task<APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse> FunctionHandler(APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyRequest input, ILambdaContext context)
{
Logger.LogInformation("Generating a new key");
var key = await KeyGenerator();
Logger.LogInformation(new Dictionary<string, object>() { { "Key", key } }, "New key generated");
Metrics.AddMetric("SuccessfulKeyGeneration", 1, MetricUnit.Count);
return new APIGatewayHttpApiV2ProxyResponse
{
Body = $@"{{""Message"":""This is your key {key}""}}",
StatusCode = 200,
Headers = new Dictionary<string, string> { { "Content-Type", "application/json" } }
};
}
Deploy the function, then navigate to CloudWatch metrics to view the results:
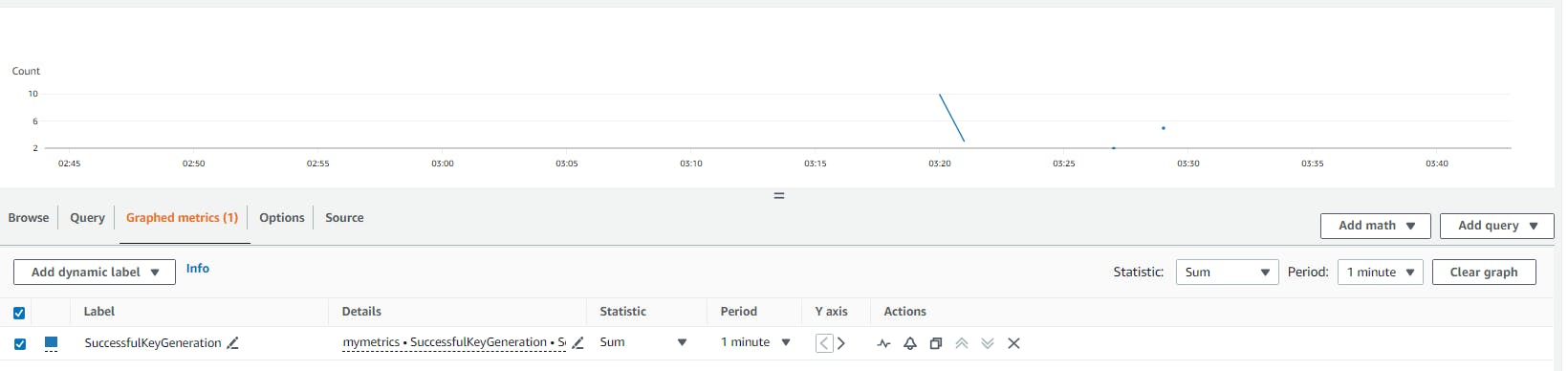
For more information, please refer to the official documentation here.
Conclusion
AWS Lambda Powertools for .NET is a collection of utilities that simplifies serverless application development. By using its logging, tracing, and metrics features, developers can concentrate on their application's core functionality. All the code is available here. Thanks, and happy coding.

