SignalR is a powerful library in the .NET ecosystem that enables real-time communication between the server and clients. In this article, we will explore how to get started with SignalR in .NET 6 by setting up a simple chat application with two types of clients. We will cover the necessary steps to configure the server, establish connections, and send messages between clients seamlessly.
Concepts
Hubs
A Hub in SignalR is a high-level pipeline that allows the server and clients to call methods on each other directly, managing connections, groups, and messaging between them.
Clients
A client in SignalR is any device or application that connects to the server and communicates with it through the hub. Clients can be web browsers, mobile apps, or other servers, and they can send and receive messages in real-time.
Transports
A Transport in SignalR is the method used for communication between the server and clients. They include
WebSockets: Full-duplex communication, low latency, and efficient use of resources. However, it may not work on older browsers or networks with strict firewalls.
Server-Sent Events (SSE): Efficient for one-way communication from server to client, with automatic reconnection. Limited to text-based data and not supported by all browsers.
Long Polling: Fallback option when WebSockets or SSE aren't available, but introduces higher latency and increased server load.
Building the Hub
Run the following commands to set up the project and solution:
dotnet new webapi -n WebAPI
dotnet new sln -n SignalRSandbox
dotnet sln add WebAPI
Open the solution and add the ChatHub.cs file with the following content:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR;
namespace WebAPI;
public class ChatHub : Hub
{
public Task SendMessage(string message, string user)
{
return Clients.All.SendAsync("ReceiveMessage", message, user);
}
}
The ChatHub class manages the communication between the client and the server. The client calls the SendMessage method, after which the server calls the ReceiveMessage method for each client. The server must be configured to pass requests to SignalR. Open the Program.cs file and update it as follows:
using WebAPI;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddCors();
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen();
builder.Services.AddSignalR();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI();
app.UseCors(cp => cp
.AllowAnyHeader()
.SetIsOriginAllowed(origin => true)
.AllowCredentials()
);
app.MapHub<ChatHub>("/chathub");
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();
Browser Client (Javascript)
Create a client.html file at the solution level with the following content:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Chat</title>
</head>
<body>
<input id="user" placeholder="User"/>
<input id="message" placeholder="Message"/>
<button id="send" type="button">Send</button>
<hr/>
<ul id="messages"></ul>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/microsoft-signalr/6.0.1/signalr.js"></script>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", () => {
const connection = new signalR.HubConnectionBuilder()
.withUrl("http://localhost:5194/chathub")
.withAutomaticReconnect()
.configureLogging(signalR.LogLevel.Information)
.build();
connection.on("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) => {
const li = document.createElement("li");
li.textContent = `${user} says ${message}`;
document.getElementById("messages").appendChild(li);
});
document.getElementById("send").addEventListener("click", async () => {
const user = document.getElementById("user").value;
const message = document.getElementById("message").value;
try {
await connection.invoke("SendMessage", user, message);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
}
});
async function start() {
try {
await connection.start();
console.log("SignalR Connected");
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
};
start();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
The script above performs the following actions:
Creates and starts a connection.
Attaches a handler to the send button, which sends messages to the hub.
Appends a handler to the connection object that receives messages from the hub and adds them to the list.
Console Client
Run the following commands to create the project and add it to the solution:
dotnet new console -n Client
dotnet sln add Client
dotnet add Client package Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR.Client
Modify the Program.cs file with the following content:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR.Client;
var connection = new HubConnectionBuilder()
.WithUrl(new Uri("http://localhost:5194/chathub"))
.WithAutomaticReconnect()
.Build();
connection.On<string, string>("ReceiveMessage", (user, message) =>
{
Console.WriteLine($"{user} says {message}");
});
try
{
await connection.StartAsync();
Console.WriteLine("SignalR Connected");
}
catch (Exception)
{
Console.WriteLine("SignalR Error");
}
Console.WriteLine("Please enter user:");
var user = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(user))
{
return;
}
while (true)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please enter message");
var message = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(message))
{
break;
}
await connection.InvokeAsync("SendMessage", user, message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
We are essentially doing the same thing as we did with the JavaScript client. The main difference lies in the input handling. Run the server and both clients and start to play with them:
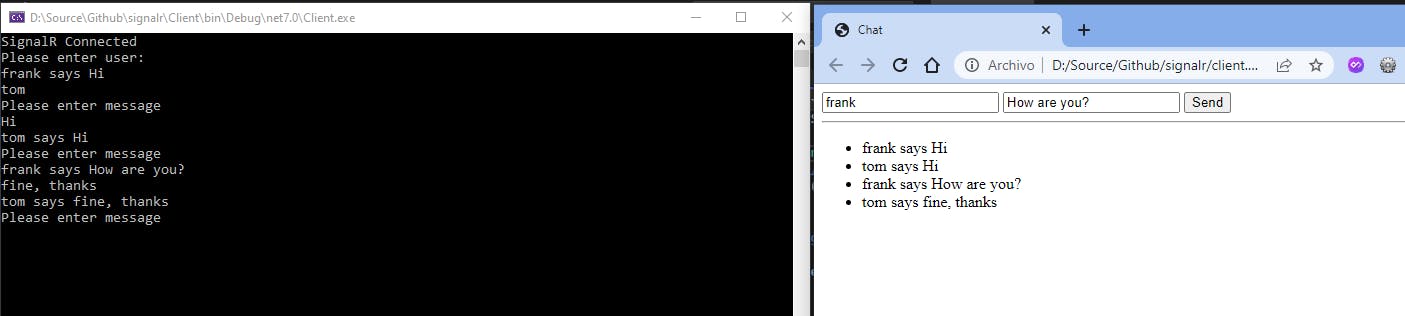
In conclusion, SignalR is a powerful library in the .NET ecosystem that enables real-time communication. With this foundation, you can explore more advanced features and build robust applications that require real-time communication like dashboards, online gaming, collaborative editing, live notifications, IoT device monitoring, instant messaging apps, and live auction platforms. All the code is available here. Thanks, and happy coding.

