Table of contents
A method for mounting files into a pod involves adding ConfigMap data to a volume, as shown below:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: myconfigmap
data:
myfile.txt: |
this is the content of the file
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mydeployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
volumes:
- name: myvolume
configMap:
name: myconfigmap
containers:
- name: mycontainer
image: myimage
volumeMounts:
- name: myvolume
mountPath: /mypath/myfile.txt
subPath: myfile.txt
However, what if the file is large or challenging to maintain within the configMap definition? Wouldn't it be great if we could embed the content of a file into the configMap definition? Fortunately, this is possible if we use Helm as a package manager for Kubernetes. Let's take the deployment of our own Technology Radar in our Kubernetes cluster as an example.
Pre-requisites
Install Docker Desktop
Enable Kubernetes (the standalone version included in Docker Desktop)
Install the Helm CLI.
Helm Chart
Run the following command to create a Helm chart:
helm create tech-radar
Create a config.csv file with the following content. Navigate to the tech-radar folder; open the values.yaml file, and modify it as follows:
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: wwwthoughtworks/build-your-own-radar
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
tag: "latest"
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""
Navigate to the templates folder and create a configmap.yaml file containing the following content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: {{ include "tech-radar.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "tech-radar.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
data:
config.csv: |
{{ .Values.configCsv | indent 4 }}
Modify the deployment.yaml as follows:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ include "tech-radar.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "tech-radar.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
replicas: {{ .Values.replicaCount }}
selector:
matchLabels:
{{- include "tech-radar.selectorLabels" . | nindent 6 }}
template:
metadata:
labels:
{{- include "tech-radar.selectorLabels" . | nindent 8 }}
spec:
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: {{ include "tech-radar.fullname" . }}
containers:
- name: {{ .Chart.Name }}
image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag | default .Chart.AppVersion }}"
imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }}
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /opt/build-your-own-radar/files/config.csv
subPath: config.csv
env:
- name: SERVER_NAMES
value: localhost 127.0.0.1
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
requests:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
Remove the remaining yaml files.
Release
Run the following command to install our chart:
helm upgrade tech-radar-release tech-radar --install --set-file configCsv="./config.csv"
We can use --set-file to set the content of a file as a value for our chart. Run kubectl describe configMap tech-radar-release to see our configMap definition.
The Application
Let's use port forwarding to test our application with the following command:
kubectl port-forward deployment/tech-radar-release 8080:80
Navigate to http://localhost:8080/ to see the application up and running. In another tab, navigate to the address http://localhost:8080/files/config.csv, use the file in the application, and enjoy your own Technology Radar:
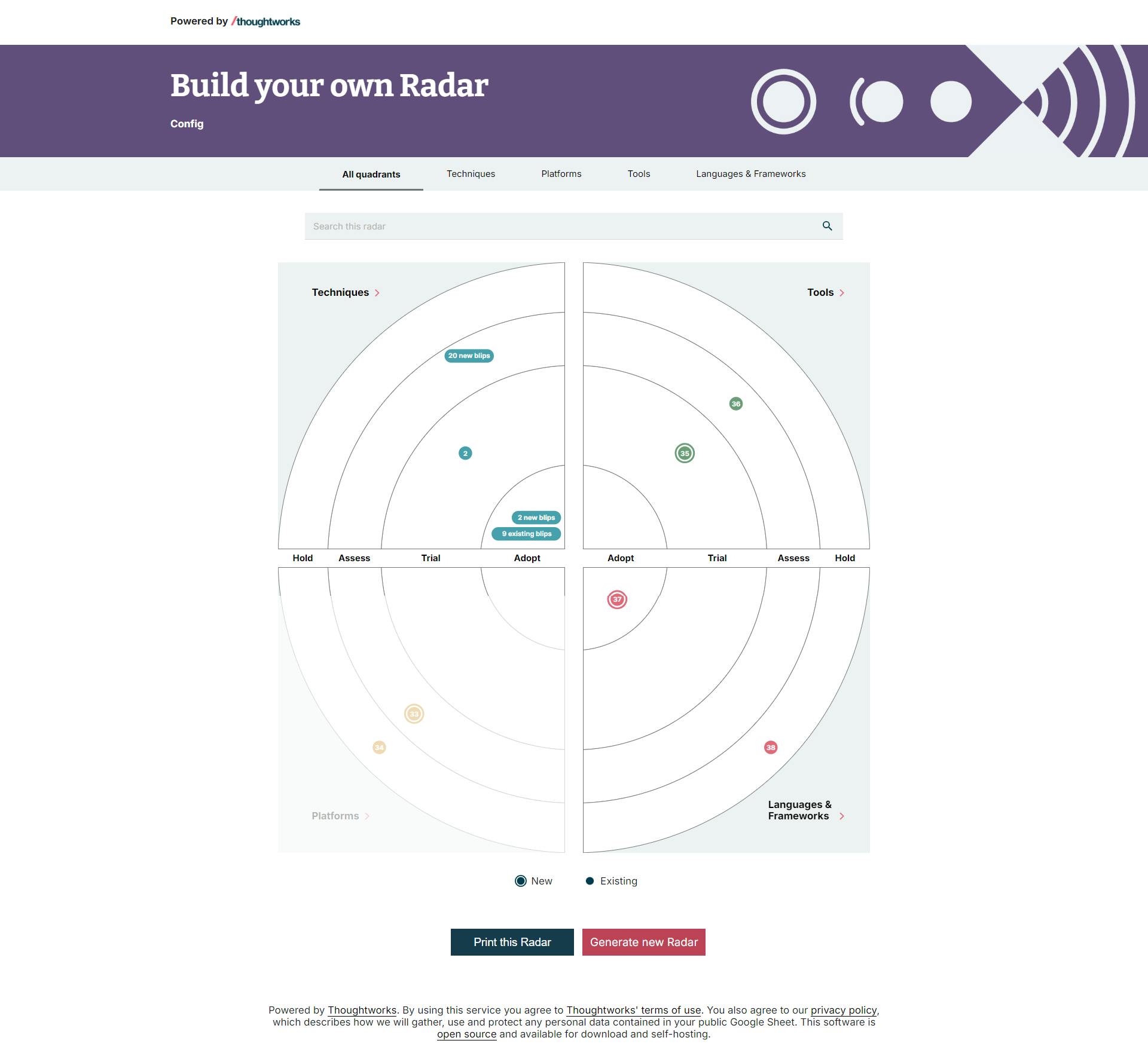
The final scripts can be found here. Thank you, and happy coding.

